
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metformin Preserves Peripheral Nerve Damage with Comparable Effects to Alpha Lipoic Acid in Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Rats (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:842-53)
- Sun Hee Kim, Tae Sun Park, Heung Yong Jin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(1):127-128. Published online January 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0289
- 3,377 View
- 98 Download
- Drug/Regimen
- Metformin Preserves Peripheral Nerve Damage with Comparable Effects to Alpha Lipoic Acid in Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Rats
- Sun Hee Kim, Tae Sun Park, Heung Yong Jin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):842-853. Published online May 28, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0190
- 6,180 View
- 177 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
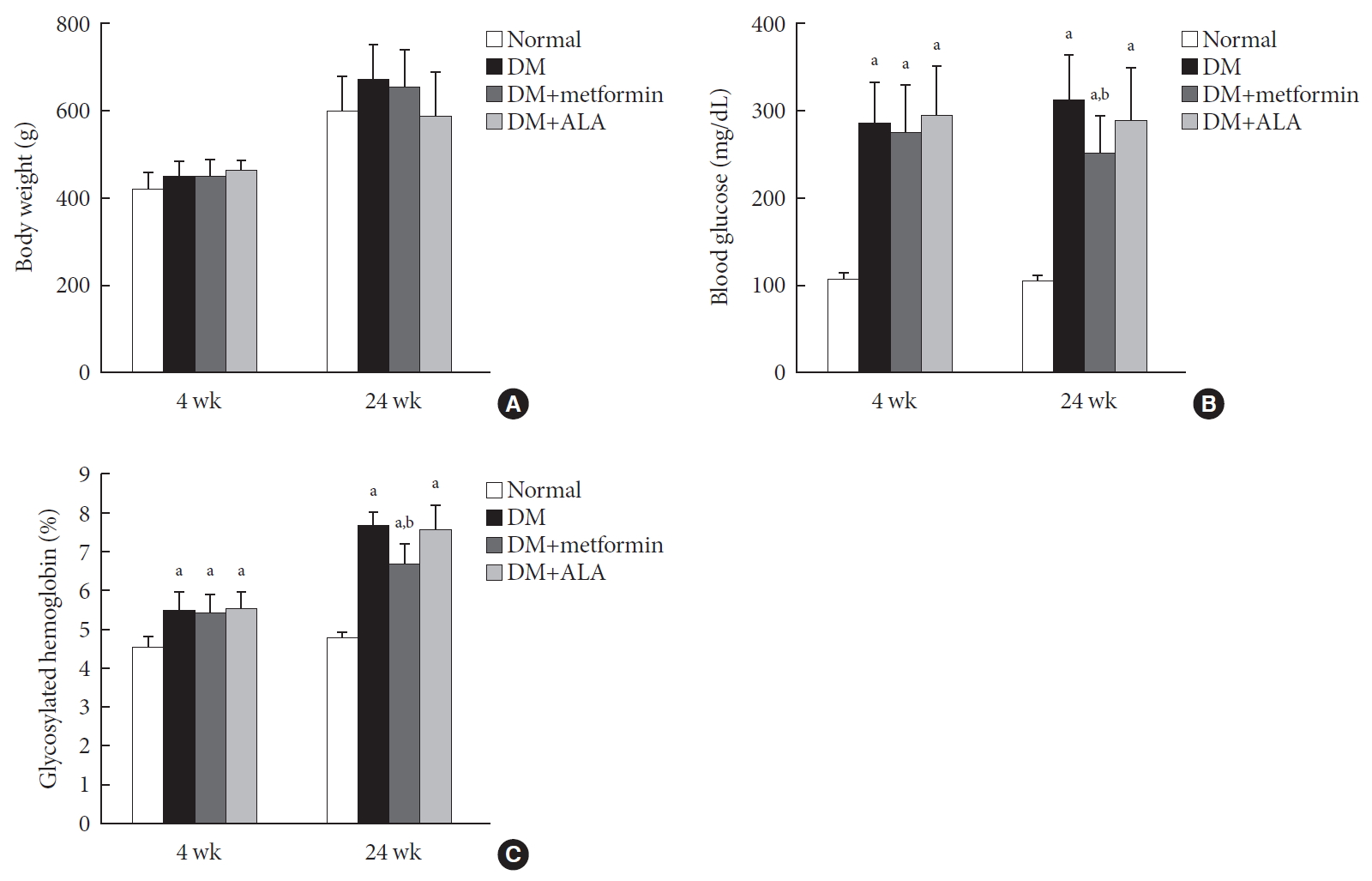
ePub Background Metformin is widely marketed medication for the treatment of diabetes, but its pharmacological effect on diabetic peripheral neuropathy remains unclear. In this study, the effect of metformin on peripheral nerves in diabetic rats was investigated using diverse neuronal parameters of nerve fibers.
Methods Rats were assigned to one of four groups (
n =7 to 10 per group): normal, diabetes mellitus (DM), DM+metformin (100 mg/kg), and DM+alpha lipoic acid (ALA, 100 mg/kg). DM was induced by streptozotocin/high-fat diet (STZ/HFD). After 12 weeks, the sensory thresholds to mechanical and heat stimuli were assessed. Repeated sensory tests, immunofluorescence microscopic comparison of peripheral nerves, and biochemical blood analysis were performed after 24 weeks.Results Both DM+metformin and DM+ALA groups showed similar trends to diverse sensory tests at 24 weeks compared to DM group although the degree of change were different according to the stimulated senses. There was no significant difference in the comparison of the intraepidermal nerve fiber density (IENFD) of peripheral nerves between the DM+metformin and DM+ALA groups (11.83±0.07 fibers/mm vs. 12.37±1.82 fibers/mm, respectively). Both groups showed preserved IENFD significantly compared with DM group (8.46±1.98 fibers/mm,
P <0.05). Sciatic nerve morphology of the experimental animals showed a similar trend to the IENFD, with respect to axonal diameter, myelin sheath thickness, and myelinated fiber diameter.Conclusion Metformin has beneficial pharmacological effects on the preservation of peripheral nerves in diabetic rats and its effects are comparable to those of ALA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metformin improves diabetic neuropathy by reducing inflammation through up-regulating the expression of miR-146a and suppressing oxidative stress
Fengmin Liu, Fangqin You, Lihang Yang, Siyun Wang, Diya Xie
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2024; 38(6): 108737. CrossRef - Effect of Metformin on the Functional and Electrophysiological Recovery of Crush Injury-Induced Facial Nerve Paralysis in Diabetic Rats
Kyung Hoon Sun, Cheol Hee Choi, Gwang-Won Cho, Chul Ho Jang
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(9): 1317. CrossRef - Is metformin neuroprotective against diabetes mellitus-induced neurodegeneration? An updated graphical review of molecular basis
Fatemeh Karami, Hamidreza Jamaati, Natalie Coleman-Fuller, Maryam Shokrian Zeini, A. Wallace Hayes, Mina Gholami, Mahsa Salehirad, Mohammad Darabi, Majid Motaghinejad
Pharmacological Reports.2023; 75(3): 511. CrossRef - Early Diagnosis through Estimation of Inflammatory Biomarkers and the Neuroprotective Role of Metformin in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Laxmi Sri, Prabhakar Orsu
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Nanotechnology(IJPSN).2023; 16(2): 6427. CrossRef - Bidirectional association between diabetic peripheral neuropathy and vitamin B12 deficiency: Two longitudinal 9-year follow-up studies using a national sample cohort
Heung Yong Jin, Kyung Ae Lee, Yu Ji Kim, In Sun Gwak, Tae Sun Park, Sang Woo Yeom, Jong Seung Kim
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(5): 436. CrossRef - An overview of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Diagnosis and treatment advancements
Jonathan M. Hagedorn, Alyson M. Engle, Tony K. George, Jay Karri, Newaj Abdullah, Erik Ovrom, Jhon E. Bocanegra-Becerra, Ryan S. D'Souza
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 188: 109928. CrossRef - The role of MicroRNA networks in tissue-specific direct and indirect effects of metformin and its application
Qinzhi Yang, Gang Wang, Dan Fang, Xiaojun Gao, Yu Liang, Liqun Wang, Jianbo Wu, Min Zeng, Mao Luo
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 151: 113130. CrossRef - Is metformin a possible treatment for diabetic neuropathy?
Juechun Wei, Yanling Wei, Meiyan Huang, Peng Wang, Shushan Jia
Journal of Diabetes.2022; 14(10): 658. CrossRef - Metformin as a potential therapeutic for neurological disease: mobilizing AMPK to repair the nervous system
Sarah Demaré, Asha Kothari, Nigel A. Calcutt, Paul Fernyhough
Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics.2021; 21(1): 45. CrossRef - Metformin Preserves Peripheral Nerve Damage with Comparable Effects to Alpha Lipoic Acid in Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Rats (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:842-53)
Bo Kyung Koo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(1): 125. CrossRef - Metformin Preserves Peripheral Nerve Damage with Comparable Effects to Alpha Lipoic Acid in Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Rats (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:842-53)
Sun Hee Kim, Tae Sun Park, Heung Yong Jin
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(1): 127. CrossRef - Impacts of statin and metformin on neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Korean Health Insurance data
Hong Ki Min, Se Hee Kim, Jong Han Choi, Kyomin Choi, Hae-Rim Kim, Sang-Heon Lee
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2021; 9(33): 10198. CrossRef
- Metformin improves diabetic neuropathy by reducing inflammation through up-regulating the expression of miR-146a and suppressing oxidative stress
- The Relationship between Anemia and the Initiation of Dialysis in Patients with Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy
- Sun Hee Kim, Kyung Ae Lee, Heung Yong Jin, Hong Sun Baek, Tae Sun Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(3):240-246. Published online April 22, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.3.240
- 3,684 View
- 32 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Anemia is associated with various poor clinical outcomes in chronic kidney disease patients. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between anemia and the initiation degree and time of dialysis in type 2 diabetic nephropathy patients.
Methods This observational retrospective study included 130 type 2 diabetic nephropathy patients in Korea. The existence of anemia, the degree and time of dialysis initiation were reviewed. Clinical characteristics and variables were also compared.
Results The levels of hemoglobin and serum creatinine were significantly correlated with the dialysis initiation (
P <0.05) during the 10-year follow-up period. Patients with anemia showed rapid decline of renal function, causing significantly more dialysis initiation (54.1% vs. 5.4%,P <0.05) compare to the patients without anemia. Average time to initiate dialysis in patients with anemia was 45.1 months (range, 8.0 to 115.8 months), which was significantly faster than that (68.3 months [range, 23.3 to 108.8 months]) in patients without anemia (P <0.01). The risk to dialysis initiation was significantly increased in patients with anemia compared to the patients without anemia (adjusted hazard ratio, 8.1; 95% confidence interval, 2.4 to 27.0;P <0.05).Conclusion Anemia is associated with rapid decline of renal dysfunction and faster initiation of dialysis in diabetic nephropathy patients. Therefore, clinicians should pay an earlier attention to anemia during the management of diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microalbuminuria as the Tip of Iceberg in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Associated Diabetic Complications
Sohaib Asghar, Shoaib Asghar, Tayyab Mahmood, Syed Muhammad Hassan Bukhari, Muhammad Habib Mumtaz, Ali Rasheed
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Association between Serum Hemoglobin and Renal Prognosis of IgA Nephropathy
Tae Ryom Oh, Su Hyun Song, Hong Sang Choi, Chang Seong Kim, Seung Hyeok Han, Kyung Pyo Kang, Young Joo Kwon, Soo Wan Kim, Seong Kwon Ma, Eun Hui Bae
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(2): 363. CrossRef - Prevalence of anemia in diabetic adult outpatients in Northeast Ethiopia
Temesgen Fiseha, Aderaw Adamu, Melkam Tesfaye, Angesom Gebreweld, Jennifer A. Hirst
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(9): e0222111. CrossRef - Targeted Clinical Metabolite Profiling Platform for the Stratification of Diabetic Patients
Ahonen, Jäntti, Suvitaival, Theilade, Risz, Kostiainen, Rossing, Orešič, Hyötyläinen
Metabolites.2019; 9(9): 184. CrossRef - Effect of high density lipoprotein cholesterol on the relationship of serum iron and hemoglobin with kidney function in diabetes
Ashley N. Williams, Baqiyyah N. Conway
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2017; 31(6): 958. CrossRef
- Microalbuminuria as the Tip of Iceberg in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Associated Diabetic Complications
- Relationship between the Korean Version Survey of the Autonomic Symptoms Score and Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy Parameters in Patients with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
- Sun Hee Kim, Kyung Ae Lee, Heung Yong Jin, Hong Sun Baek, Tae Sun Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(5):349-355. Published online October 17, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.5.349
- 5,186 View
- 51 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The Survey of Autonomic Symptom (SAS) scale was reported as an easy instrument to assess the autonomic symptoms in patients with early diabetic neuropathy. In this study, we investigated the relationship between the SAS scale and the parameters of cardiac autonomic neuropathy (CAN) in Korean patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN).
Methods The SAS scale was tested in 30 healthy controls and 73 patients with DPN at Chonbuk National University Hospital, in Korea. The SAS score was compared to the parameters of the CAN test and the total symptom score (TSS) for DPN in patients with DPN.
Results The SAS symptom score and total impact score were increased in patients with DPN compared to the control group (
P =0.01), particularly in sudomotor dysfunction (P =0.01), and vasomotor dysfunction (P =0.01). The SAS score was increased in patients with CAN compared to patients without CAN (P <0.05). Among the diverse CAN parameters, the valsalva ratio and postural hypotension were associated with the SAS score (P <0.05). However, there was no association between the SAS scale and TSS for DPN, and TSS for DPN did not differ between patients with and without CAN.Conclusion SAS is a simple instrument that can be used to assess autonomic symptoms in patients with diabetes and can be used as a screening tool for autonomic neuropathy, particularly for CAN.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Autonomic neuropathic symptoms in patients with diabetes: practical tools for screening in daily routine
Ana Raquel Souza de Azevedo Vieira, Lara Benigno Porto-Dantas, Flaviene Alves do Prado Romani, Patrícia Souza Carvalho, Rodica Pop-Busui, Hermelinda Cordeiro Pedrosa
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Symptomatic diabetic autonomic neuropathy in type 1 diabetes (T1D): Findings from the T1D exchange
Kara Mizokami-Stout, Ryan Bailey, Lynn Ang, Grazia Aleppo, Carol J. Levy, Michael R. Rickels, Viral N. Shah, Sarit Polsky, Bryce Nelson, Anders L. Carlson, Francesco Vendrame, Rodica Pop-Busui
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2022; 36(5): 108148. CrossRef - Clinical Assessment Scales in Autonomic Nervous System Disorders
Eun Bin Cho, Ki-Jong Park
Journal of the Korean Neurological Association.2021; 39(2 Suppl): 60. CrossRef - Peripheral Nerve Conduction And Sympathetic Skin Response Are Reliable Methods to Detect Diabetic Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy
Xiaopu Lin, Chuna Chen, Yingshan Liu, Yu Peng, Zhenguo Chen, Haishan Huang, Lingling Xu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive model to identify the risk of losing protective sensibility of the foot in patients with diabetes mellitus
Esther Chicharro‐Luna, Francisco José Pomares‐Gómez, Ana Belen Ortega‐Ávila, Ana Marchena‐Rodríguez, José Francisco Javier Blanquer‐Gregori, Emmanuel Navarro‐Flores
International Wound Journal.2020; 17(1): 220. CrossRef - The hemodynamic and pain impact of peripheral nerve block versus spinal anesthesia in diabetic patients undergoing diabetic foot surgery
Hou Yee Lai, Li Lian Foo, Siu Min Lim, Chen Fei Yong, Pui San Loh, Sook Hui Chaw, Mohd Shahnaz Hasan, Chew Yin Wang
Clinical Autonomic Research.2020; 30(1): 53. CrossRef - Update on the Impact, Diagnosis and Management of Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy in Diabetes: What Is Defined, What Is New, and What Is Unmet
Vincenza Spallone
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(1): 3. CrossRef - Validation of the Composite Autonomic Symptom Score 31 (COMPASS 31) for the assessment of symptoms of autonomic neuropathy in people with diabetes
C. Greco, F. Di Gennaro, C. D'Amato, R. Morganti, D. Corradini, A. Sun, S. Longo, D. Lauro, G. Pierangeli, P. Cortelli, V. Spallone
Diabetic Medicine.2017; 34(6): 834. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Autonomic Dysfunction Predicts Diabetic Foot Ulcers in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Without Diabetic Polyneuropathy
Jae-Seung Yun, Seon-Ah Cha, Tae-Seok Lim, Eun-Young Lee, Ki-Ho Song, Yu-Bae Ahn, Ki-Dong Yoo, Joon-Sung Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko
Medicine.2016; 95(12): e3128. CrossRef - Retinal Neurodegeneration Associated With Peripheral Nerve Conduction and Autonomic Nerve Function in Diabetic Patients
Kiyoung Kim, Seung-Young Yu, Hyung Woo Kwak, Eung Suk Kim
American Journal of Ophthalmology.2016; 170: 15. CrossRef - Screening of Autonomic Neuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Bo Kyung Koo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(5): 346. CrossRef
- Autonomic neuropathic symptoms in patients with diabetes: practical tools for screening in daily routine
- Effects of 'Ubiquitous Healthcare' on the Ability of Self-Management in Elderly Diabetic Patients.
- Sung Hoon Yu, Sun Hee Kim, So Yeon Kim, Sung Hee Choi, Soo Lim, Yoon Seok Chang, Hak Jong Lee, Young Joo Park, Hak Chul Jang
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(1):58-64. Published online February 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.1.58
- 2,266 View
- 20 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The need for a new healthcare system is growing due to the paradigm shift from health supervision to health maintenance. Previously, we performed a pilot study that examined the effectiveness of a ubiquitous healthcare (U-healthcare) diabetes management program which consists of self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) and mobile phone services for elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. In this study, we investigated the effect of a diabetes management program using U-healthcare based on the self-care skills of elderly patients with diabetes mellitus. METHODS: From July to October 2005, 17 patients were recruited and provided with a blood glucometer with the ZigBee module and a mobile phone. In addition, the patients' understanding of diabetes self-care skills was examined at the beginning and end of the study. At the end of the study, we determined the level of patient satisfaction regarding U-healthcare services. RESULTS: The patients' test scores on their understanding of diabetes mellitus improved from 57.2 +/- 20.7 to 72.7 +/- 13.4%. Specifically, patient knowledge of the basic principles for a proper diabetic diet (52.9% vs. 82.4%, P = 0.046), foods that influence blood sugar level (41.2% vs. 76.5%, P = 0.007) and the influence of beverage choice (41.2% vs. 64.7%, P = 0.007), all increased. In addition, a significant increase in knowledge of living standards regarding diabetes mellitus was observed (64.7% vs. 88.2%, P = 0.0032). CONCLUSION: We conclude that the U-healthcare incorporating SMBG could be promising, as it improves self-management skills of diabetes mellitus patients, as well as their understanding of the disease. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Self-management of Chronic Conditions Using mHealth Interventions in Korea: A Systematic Review
Jae Yoon Yi, Yujin Kim, Yoon-Min Cho, Hongsoo Kim
Healthcare Informatics Research.2018; 24(3): 187. CrossRef - Effectiveness of the Smart Care Service for Diabetes Management
Young-Soon Chung, Yongsuk Kim, Chang Hee Lee
Healthcare Informatics Research.2014; 20(4): 288. CrossRef - Ubiquitous Healthcare Service Has the Persistent Benefit on Glycemic Control and Body Weight in Older Adults With Diabetes
Seon Mee Kang, Min Joo Kim, Hwa Young Ahn, Ji Won Yoon, Min Kyong Moon, Hye Seung Jung, Sung Hee Choi, Soo Lim, Kyong Soo Park, Hak C. Jang
Diabetes Care.2012; 35(3): e19. CrossRef - Improved Glycemic Control Without Hypoglycemia in Elderly Diabetic Patients Using the Ubiquitous Healthcare Service, a New Medical Information System
Soo Lim, Seon Mee Kang, Hayley Shin, Hak Jong Lee, Ji Won Yoon, Sung Hoon Yu, So-Youn Kim, Soo Young Yoo, Hye Seung Jung, Kyong Soo Park, Jun Oh Ryu, Hak C. Jang
Diabetes Care.2011; 34(2): 308. CrossRef - A Survey on Ubiquitous Healthcare Service Demand among Diabetic Patients
Soo Lim, So-Youn Kim, Jung Im Kim, Min Kyung Kwon, Sei Jin Min, Soo Young Yoo, Seon Mee Kang, Hong Il Kim, Hye Seung Jung, Kyong Soo Park, Jun Oh Ryu, Hayley Shin, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(1): 50. CrossRef
- Self-management of Chronic Conditions Using mHealth Interventions in Korea: A Systematic Review

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





